What is electronic data interchange?
The term electronic data interchange (EDI) refers to the exchange of structured electronic business documents between different business partners. EDI is not a specific technology, but an interaction of electronic processes, exchange protocols and business document standards with ultimately one central goal:
“Automated communication of information, in the form of business documents directly between two IT systems, without human intervention”.
This seamless and direct communication enables a high process automation, as business information can be exchanged between different systems quickly and without the need for PDFs/paper. Direct means that no change of the information-carrying medium is necessary during the exchange (such as the manual typing of a paper bill). The data is transferred directly from one system to the other without anyone having to intervene manually.
What is being exchanged between systems in the context of electronic data interchange? Depending on the application, this can be electronic orders, delivery notes and invoices, but also master data or sector- or industry-specific data such as transfers, delivery schedules, time lists, personal data, etc.
The steps involved in a typical exchange
Sending a paper invoice involves several steps on both the supplier’s and the receiver’s side. For the supplier the invoice needs to be generated, printed and posted. The supplier then has to wait for the document to reach their partner.
On the receiver’s side, they must first wait for the invoice to arrive. Following this, the necessary data must be manually entered into their accounting system.
In addition to being a costly and time-consuming method, the manual effort involved in exchanging paper documents can lead to errors and inconsistencies in data – a problem that can quickly escalate in fast-moving modern supply chains.
Avoiding manual effort
To avoid some of the issues with exchanging paper documents, many businesses exchange information digitally via email in the form of PDFs, word processing documents and spreadsheets. However, while this is marginally more efficient than sending physical documentation, the same key issues remain. The sender may still need to send the document manually and the receiver is still required to extract and log the relevant data themselves, all of which requires time and effort.
With EDI, the issue of manual data entry and message sending and receiving is removed completely, leading to far more streamlined supply chains.
EDI languages
With an EDI solution, relevant data is translated into a simple computer-readable language and sent directly to your partner’s system, which automatically extracts the data and stores it in the relevant place.
These EDI “languages” are text files, which condense all the necessary information into as simple and small a message as possible. To guarantee that both sender and receiver understand what is being sent and received, the content of these EDI files follows strict rules. These rules are defined in EDI standards. The two most common EDI standards are UN/EDIFACT and ANSI ASC X12, which are both delimiter-based standards. Many EDI messages are also exchanged using XML. Other widely used formats and standards also include CSV files and TRADACOMS documents (which are particularly popular in the UK).
How does EDI streamline supply chains?
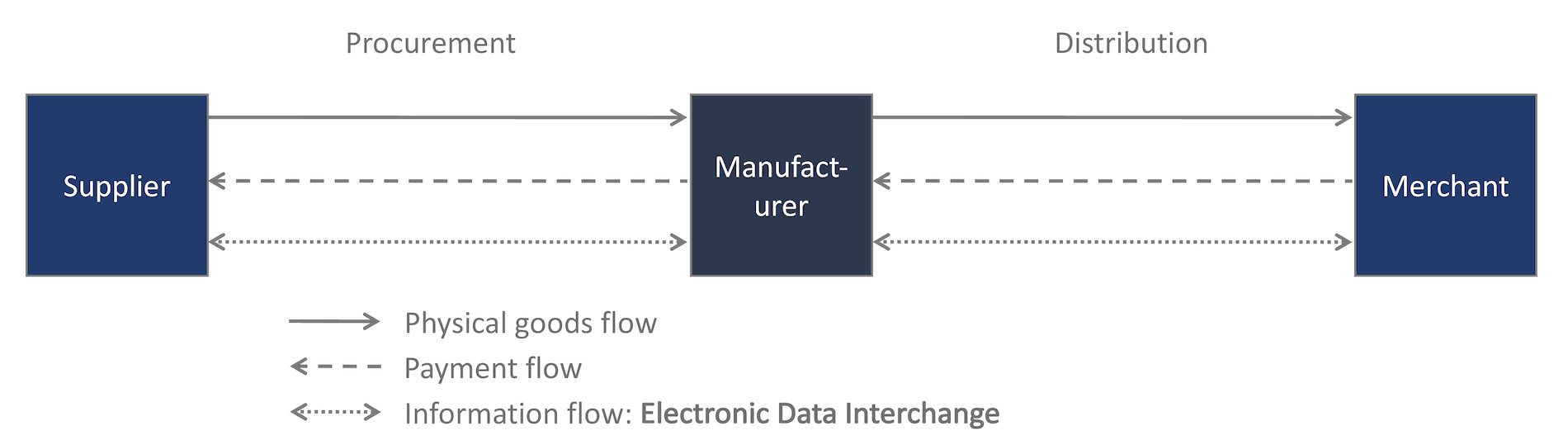
Particularly in the area of supply chain management, the use of EDI plays a very important role. The following figure shows a simplified representation of a typical supply chain scenario. For a supply chain, one thinks primarily of the flow of goods and payments. However, it is only the flow of information that makes the supply chain possible in the first place.
This flow of information was dominated by classical supply chains of paper and telephone. Later, new media such as fax or email were added.
When it came to the quantity to be ordered, the experience of the partners involved played a role – as in a classic convenience store in the 1950s.
The owners knew approximately about the expected sales and tried to manage the restocking accordingly. But, it often it came to misjudgements – then the product was simply not available, and the consumer had to wait until the goods were available again. This is an unthinkable scenario for today’s modern commerce.
The requirements for supply chains increased continuously in the industrial sector as well. Today’s supply chains have reached such high complexity and speed that the use of manual and unstructured information exchange is no longer possible.
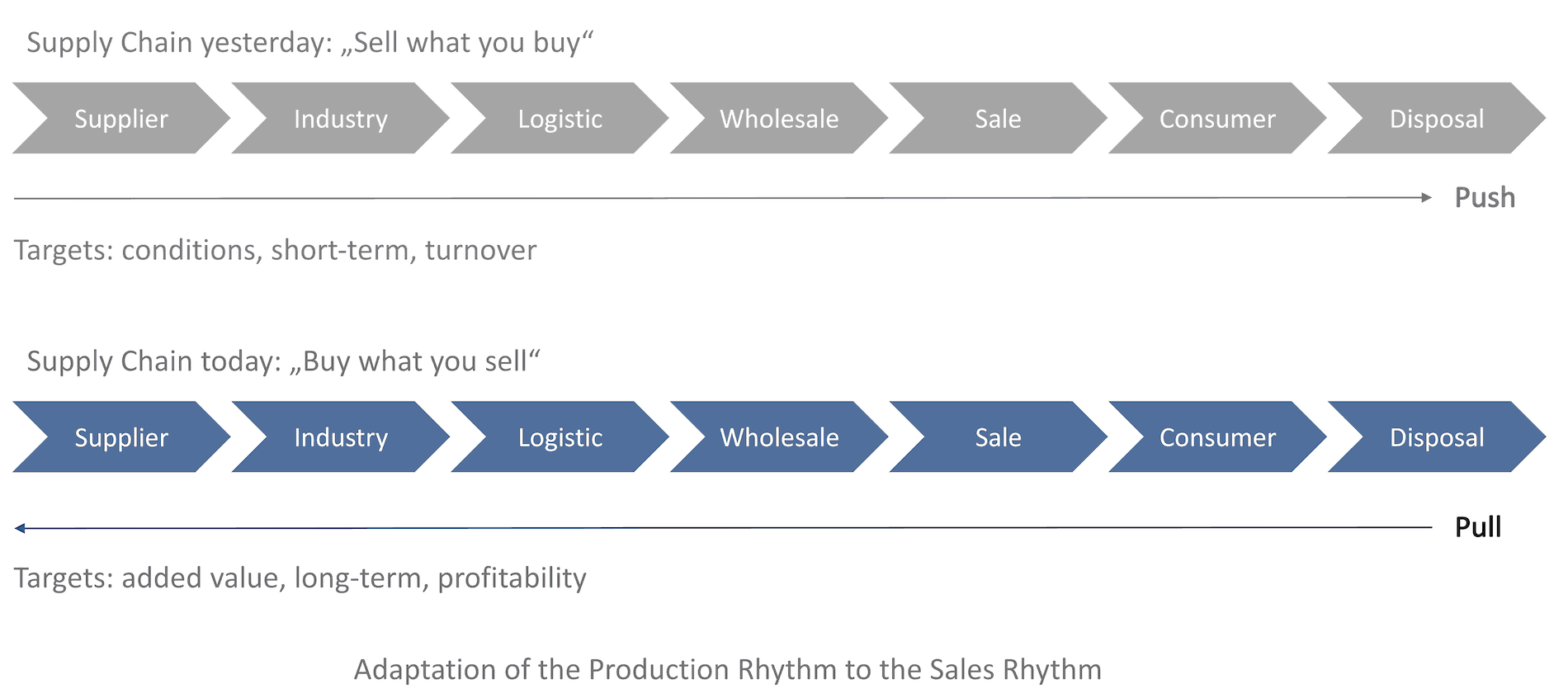
Earlier supply chains were characterised by the motto “sell what you buy”. Producing companies bought production resources, produced products and passed them on to buyers. These processes were characterised by a “push” because the sub-suppliers pushed products to the buyers. If they did not need it, the subcontractors were stuck with their stocks. Conversely, there was also the case that the demand of the buyers could not be satisfied by the offer of the producers, because too little was produced.
Supply Chains Yesterday and Today
Modern supply chains are characterized by a very close integration of the participating partners, in which customers communicate detailed forecasts of the anticipated demand for the pre-suppliers. The core motto is therefore “buy what you sell”. Products are no longer “pushed” by the producers, but “pulled” by the customers. Producers can plan production accordingly and avoid inventories which are too large or incorrect deliveries due to missing stocks.
Modern supply chains, such as those found in trade or in the automotive industry (especially just-in-time and just-in-sequence), would not be possible without the use of electronic data interchange.
What are the benefits of electronic data interchange?
As we explore in our infographic, EDI offers many significant benefits. In particular, the automation of business processes through EDI brings an extensive list of benefits in daily operations. For example:
- Faster transmission times
- Lower transmission costs
- Reduction of repeated input
- Reduction of data entry errors
- Increase the accuracy of the information
- Reduction of the paper-based document flow
- Cost savings in data handling activities
- Increasing the processing speed
- Reduction of storage costs (e.g. just-in-time or just-in-sequence)
- Avoid duplication
- Reduction of running times
- Time reduced operations
Further, EDI can also allow businesses to benefit in many other ways by ensuring that business-relevant information is available more quickly and, above all, in a structured way. The evaluation of this data by appropriate business intelligence methods enables an improved process control by data which is constantly available and up-to-date.
The impact of data visibility
In addition to providing benefits relating to automation and decision-making, the best EDI systems will be able to offer greatly improved data visibility. With such a system, users may be able to access helpful information such as whether or not their partners have received or acknowledged a certain message in real time. Similarly, real-time data visibility ensures that amendments and adjustments to key B2B exchanges (such as orders and order responses) can be handled quickly and easily. For example, were the sender of a certain message to alter any information, the receiver’s system may be able to update the relevant record automatically in log form (like a ledger) and alert the relevant users immediately to the change. Technically this would be achieved using a purchase order change EDI message.
The role of EDI today
Decades ago electronic data interchange was only used by very large supply chain businesses as the technical setup and maintenance of EDI connections had to be handled completely in-house by specialised teams. Today, however, thanks to the emergence of cloud-based software, the benefits of EDI can be enjoyed by all businesses regardless of size or EDI know-how.
As well as private companies, governments too are turning to data exchange automation in an attempt to reduce costs – particularly those relating to electronic invoicing. As a result, across Europe in particular, new legislation means that having a reliable EDI solution may soon move from being a necessity for large businesses to being a necessity for all businesses.
While it may have been possible for supply chain businesses to survive without a comprehensive EDI solution in the past, this is no longer the case. Without an EDI solution companies risk…
- Loss of business
- Loss of reputation
- Impaired planning ability
- Impaired ability to make informed decisions
- Lack of flexibility
- Non-compliance with new automation regulations
Want to harness the power of successful EDI?
At ecosio, we’ve helped hundreds of businesses to streamline their supply chains and experience the benefits of automated B2B communication.
Through our comprehensive service, which includes building and testing all required mapping and routing, managing partner onboardings from start to finish, and round-the-clock monitoring, we ensure that minimal internal effort is required to achieve an optimal solution. In short, our EDI experts take care of everything so you can focus on what you do best! This way, we not only save
you time and money, but also reduce risk and boost your competitive advantage. If you’re interested in consolidating complex existing processes into one unified cloud-based system, our flexible Integration Hub and fully managed, modular services offer the perfect answer to your problems by providing Connections That Work.
Interested in learning more? Then contact us today!
Image credits
- Convenience Store, 1950s: GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2, via Wikimedia Commons