ANSI ASC X12 is the second major EDI format standard besides UN/EDIFACT and offers some special features in structure and design. In this article we therefore focus on the segments and elements in the structure of an ANSI X12 file.
For more information on using X12 party identifiers correctly, please see our article “The Most Common ANSI ASC X12 Parties and How to Use Them” on this topic.
Segments as basis in the structure of an ANSI X12 file
EDI files essentially consist of segments that contain the basic information. Every EDI message is created from these segments, as with ANSI ASC X12. For example, if we simply want to send the name of a partner company, we can use the so-called NM1 segment (easy: NM stands for “name”).
Our example segment could now look like this:
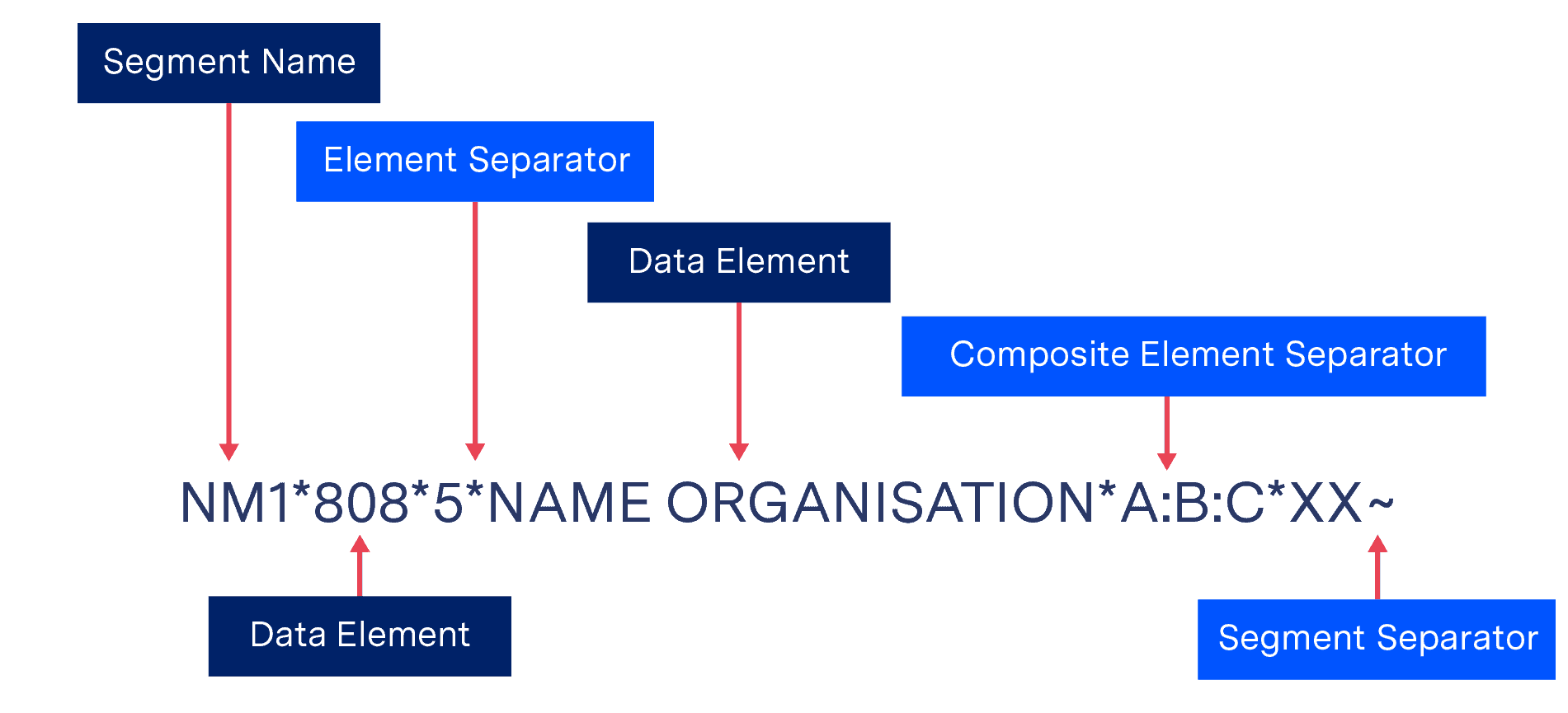
Structure of an ANSI X12 file Example of an ANSI X12 segment
Designations
Segment Name: Stands for the name of the segment. NM1
Element Separator: For separation before data elements. *
Segment Separator: This determines the end of the segment. ~
Data Element: Specified data. 808, 5, NAME ORGANISATION, XX
Composite element: Several data elements can be grouped into a logical unit. A:B:C
Composite Element Separator: Composite elements can be separated. :
The delimiters for the correct reading (“parsing”) of the data or data elements by the EDI solution are element separator, segment separator and composite element separator. Data elements can, for example, simply be text (such as our example company), numbers, time or date specifications, identifiers, etc. Data elements have a certain minimum and maximum length. For example, text is usually longer than a time specification. EDI parsers can also check the permitted length in the structure of the ANSI X12 file.
The ISA segment in the structure of an ANSI X12 file
At the beginning of an EDI file there is the ISA segment, also called Interchange Control Header. The delimiters or separators mentioned above, which the EDI solution uses to divide and read the segment, are determined here and communicated to the EDI solution.
This works because the ISA segment is defined at exactly 106 characters. This means that the EDI solution can search for the character itself at the corresponding position in the segment:
ISA*00* *00* *01*069167604 *ZZ*PLANT-MX *170614*0808*^*00401*000000003*0*T*:~'
Data Element Separator: Character No. 4: *
Repetition Element Separator: (for repeating data elements): Character no. 83: ^ (U would stand for “unused” by the way)
Composite Element Separator: Character Nr. 105: :
Segment Separator: Character Nr. 106: ~
When the structure of an ANSI X12 file becomes more complicated
EDI messages can sometimes become very large. To counteract the complexity, two elements were created for ANSI X12:
Composite Elements
Sometimes a single data element is not specific enough for a message. Then a composite element can be used to help. This is defined in the ISA (Interchange Control Header) segment at the very beginning of a complete EDI message, which we will discuss below. In our case it is :. The EDI solution can then recognize such data elements in the composite and distinguish them by the character.
Recurring elements
With version 5010 X12, repeating data elements (repeating elements) can also be defined. This allows information to be specified more specifically in a segment by using the same data element for more information. This also works with composite data elements. The separator for the EDI solution is again defined in the ISA segment.
For example, we have a CLM segment (CLM stands for “claim”) whose element CLM05 consists of three components: Claim Facility Code Value, Claim Facility Code Qualifier and Claim Frequency Type Code. CLM05 is represented as a composite element with 11:B:1:
CLM*A37YH556*500***11:B:1^12:B:2*Y*A*Y*I*P.
This is now, indicated by ^, cemented with a new composite element 12:B:2.
More questions?
If you have questions about ANSI X12 or EDI more generally, please contact us. We are always happy to help!
More information can also be found on the official ANSI ASC X12 homepage is also worth a click.