Overview of SAP ERP
The SAP Business Suite is SAP’s core product. It consists of several solutions, which can be purchased either together or separately.
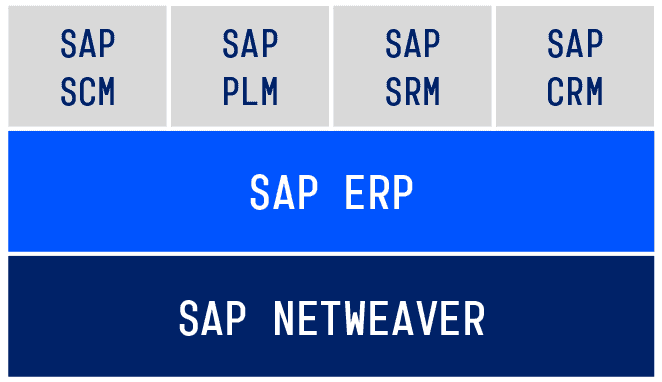
Structure of the SAP Business Suite
The technical foundation is SAP NetWeaver, on which all other modules and components are based. SAP ERP is the central component and offers functions for the following fields:
Logistics (SAP ERP Operations and SAP ERP Corporate Services)
- Real estate management (component RE)
- Production planning & control (component PP)
- Warehouse management (component WM)
- Customer service (component CS)
- Plant maintenance (component EAM/PM)
- Environment, health & safety (component EH&S)
- Logistics execution (component LE)
- Quality management (component QM)
- Sales & distribution (component SD)
- Materials management (component MM)
Accounting (SAP ERP Financials)
- Treasury (component TR)
- Project system (component PS)
- Controlling (component CO)
- Financial accounting (component FI)
- Enterprise controlling (component EC/SEM)
- Financial supply chain management (component FSCM)
Human Resources (SAP ERP Human Capital Management)
- Organisation management (component OM)
- Travel management (component TM)
- Recruitment (component RC)
- Personnel time management (component PT)
- Personnel planning and development (component PD)
- Personnel administration (component PA)
- Payroll (component PY)
- Personnel events (component PE)
The advanced modules can be found in the top layer of the SAP Business Suite. They are intertwined with SAP ERP and offer additional functions. Let’s first look at SAP ERP before looking at the single modules.
Logistics – SAP ERP SC
The SAP ERP SC (Supply Chain) maps the processes of a company’s entire logistics chain and is therefore very extensive. It consists of several components.
The SAP component MM (Materials Management) supports the purchasing of goods and services. It includes functions such as the processing of requisitions, inventory management and the maintenance of material master data.
The component PP (Production Planning & control) is used for sales and production planning, as well as an assembly process.
SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) covers the processes of selling goods or services of a company. It also provides solutions for foreign trade and customs clearance.
Finally, SAP CS (Customer Service) provides the most important functions for customer service, such as the processing of customer service orders.
Accounting – SAP ERP FI
The SAP ERP Financials covers internal and external financial accounting, corporate governance, treasury and receivables management.
Financial accounting and business transactions, among other things, are documented in order to produce the yearly balance sheet and the profit/loss account can be prepared (GuV).
The SAP component CO (Controlling) supports the internal accounting of a company. It allows the collection of economically important information based on cost, performance and investment calculation.
SAP ERP Financials is also responsible for other important tasks, e.g. the creation and planning of financial resources (Treasury), as well as the securing of liquidity through receivables management.
Human Resources – SAP ERP HCM
SAP ERP HCM (Human Capital Management) helps companies manage processes concerning their employees. Each employee is saved with a so-called infotype record. This record contains all important information about the employee, as well as their job title within the company. SAP ERP HCM can also record an employee’s working hours and create their payrolls. The entire course of training and further education for employees is also covered.
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
Special modules in detail
Now let’s look at the top layer of the SAP Enterprise Suite: the SAP modules. These partly overlap with the functions from SAP ERP. However, these modules offer a wider range of functions to address a business’s more specific needs.
Supply Chain Management – SAP SCM
SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) offers advanced logistics functions from SAP ERP. SAP SCM is suitable for the entire supply chain: from the supplier to the customer. The SAP SCM functions include warehouse management, transportation management, supply chain planning and optimisation, and RFID processes (Radio Frequency Identification).
Product Lifecycle Management – SAP PLM
SAP Product Lifecycle Management (SAP PLM) represents the lifecycle of a product beginning with an idea through the production, and later to customer service. This module is very popular in the manufacturing sector, as it simplifies the internal and external communication through the exchange of information, plans, instructions, etc…
Supplier Relationship Management – SAP SRM
Businesses who work with many different suppliers can optimise their relationships with them using the Supplier Relationship Management (SAP SRM). Suppliers are more closely involved in the purchasing processes, which helps plan and manage the relationships in a more efficient way.
SAP Customer Relationship Management – SAP CRM
SAP Customer Relationship Management (SAP CRM) is responsible for the active customer relationship management and supports the communication between different departments and the customer. The customer information is given to the marketing department, sales and service, which in return allows them to fill the needs of the customer and react accordingly. Various analytic functions offer a deeper insight into customer behaviour and enable the development of efficient marketing strategies.
Special industry solutions
In response to the needs of different industries, SAP offers customised solutions in addition to the standard solutions. For this purpose, special functions are added on to enhance the standard processes of the respective industry. There are now over 20 industry solutions, including:
- Process industry (e.g. SAP for Oil and Gas)
- Service provider (e.g. SAP for Retail)
- Manufacturing industry (e.g. SAP for Automotive)
- Administration and finance services (e.g. SAP for healthcare or Banking)
Extensions to an SAP system
Thanks to the NetWeaver Stack, an SAP system is very flexible when it comes to the implementation of company-specific requirements and the integration from third party software. Therefore, almost all SAP modules can be provided with extensions, as long as they are programmed with ABAP.
If a specific functionality is needed, it is possible to implement the systems of third-party providers, such as an EDI provider, into the SAP ERP system.
Summary
SAP ERP already offers an extensive amount of basic functions for businesses of different industries. Depending on the requests, new modules can be added. This gives businesses the possibility to optimise control and have an overview in the logistics, accounting and human resource areas.
Questions?
Do you still have questions about SAP or implementing EDI into your ERP system? Feel free to contact us, we would love to help you!
Alternatively, you can find lots of relevant SAP content in our resource centre.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.