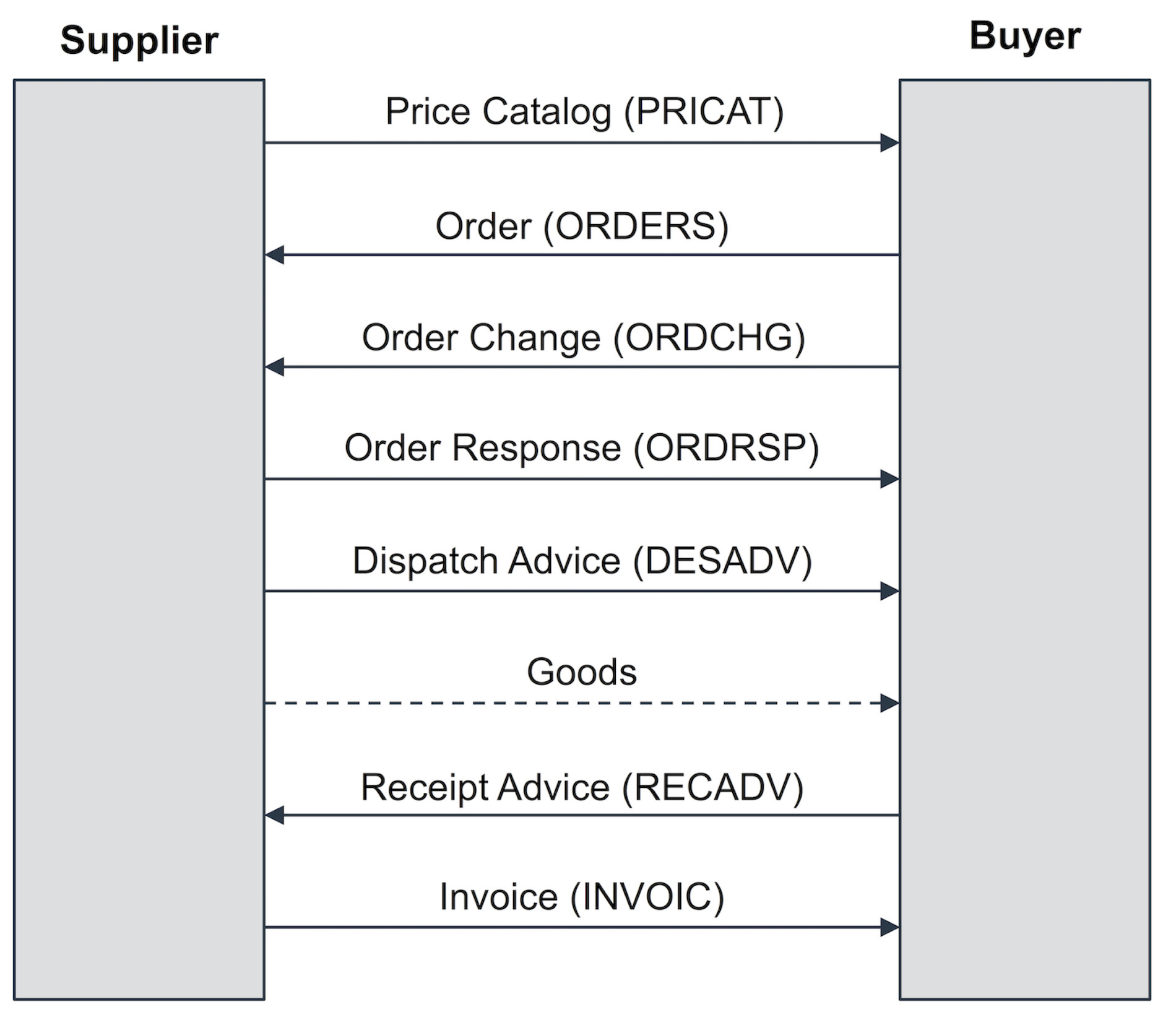
Typical trading partner cycle, EDI process and common critical documents
The exchange of business documents is part of a procurement process between suppliers and buyers, whether in retail, automotive or other production industries transacting goods and services on a regular basis. The following figure represents the typical flow of the seven most common EDI documents between a buyer and seller in a trading partner cycle, which I will explain further below.
buyer and seller in a trading partner cycle
Price Catalog (PRICAT)
The first step of the exchange process between trading partners, is the price catalog and is required when the supplier provides the buyer with a current list of its products, product details, as well as price information. This process is commonly referred to as the product master data exchange, however, is not that common in modern trading partner cycles.
Purchase Order (ORDERS)
Once a buyer decides on the parameters of purchase from its supplier, the buyer must send a purchase order in order to receive those good. As such, this document is a necessary EDI transaction used by a customer, e.g. Sainsbury’s or Skanska, to place an order with one of its suppliers, e.g. Nestle or Tata Steel. This will contain the same information included in a traditional paper purchase order (PO), such as specific items and quantities to be produced, pricing and applicable discounts and shipping details. With EDI, the message includes coded information about the buyer, supplier, delivery point, products, etc. This means that unique identifiers such as global location numbers (GLNs) or global trade identification numbers (GTINs) are used for the identification of the involved trading partners and their goods. GLNs and GTINs are mostly found in retail and wholesale – manufacturing and the automotive industry often build on supplier’s or customer’s article numbers for material identification. In regard to partner identification bilaterally agreed IDs (e.g. JLR for Jaguar Landrover) or DUNS numbers are often used.
The benefit of using purchase orders via EDI allows businesses to avoid data entry errors associated with manually entering data into your system. It also reduces time delays and speeds up the process of sending and receiving documents, as well as, eliminating duplicates.
Order Change (ORDCHG)
A buyer may wish to request to change the quantity of goods ordered or the requested delivery date by emitting an order change message, indicating to the supplier a change of the initial purchase order.
Order Response (ORDRSP)
The supplier may acknowledge a received order message or a received order change message using an order response message. The order response can also be used as an Order Confirmation so as to recap and confirm what was in the purchase order. The supplier is essentially telling the customer that the order was received and they will take the job. It closes the loop and confirms the order electronically, without a follow up call or fax. The document can also indicate that the purchase order was accepted or rejected. It can even indicate any changes in pricing or quantity, alert the customer of product availability (in stock or backorder) and provide ship and delivery dates.
An automatic update of confirming an order or response will prevent confusion or mistakes when the invoice is sent later down the line. Time and money is saved by not having to follow up manually and check.
Dispatch Advice (DESADV)
A supplier notifies the buyer of the shipped good the buyer can expect to receive. Using the dispatch advice message, the supplier provides the buyer with information about the shipment including number of pallets, pallet identification numbers such as serial shipping container codes (SSCC), net and gross weight, identification of the transport vehicle such as license plate number of the truck, etc.
The benefit of this is that the buyer may coordinate the arrival and processing of the goods-to-arrive, e.g., in case of cross-docking-scenarios, frozen goods, etc. Furthermore, the buyer may verify the completeness of the shipment by comparing the received goods with the information provided in the previously received dispatch advice message.
Receipt Advice (RECADV)
After the goods have been received by the buyer, the buyer may emit a receipt advice message, confirming the amount of received goods. The amount of confirmed goods in the receipt advice may be different from the amount communicated by the supplier in the dispatch advice. Reasons for such a deviation may for instance be damaged goods the buyer refuses to accept or a wrong number of goods shipped by the supplier.
Invoice (INVOIC)
An outbound EDI document that replaces the traditional paper invoice. This document basically says that your order is complete and has shipped, so now we are billing you. Invoice details typically include goods provided, shipping particulars and payment terms. If your EDI is embedded, the invoice data is usually translated directly out of your accounts receivable module into the EDI document and subsequently into the accounts payable module of the customer.
Questions about the trading partner cycle of document types?
If you’d like more help with gathering your requirements from your supply chain, you can reach out – we’d be happy to help. or check out our chat.