🔍 TL;DR summary
- Self-service connectors allow suppliers to configure their own e-invoicing connection without relying on technical teams, speeding up onboarding
- These tools reduce setup struggles by automating processes, minimising manual intervention, and providing guided configuration steps
- Benefits include faster supplier activation, fewer errors during setup, and lower demands on internal resources
- Self-service connectors support multiple document formats and transmission protocols, enabling flexible integration with various customer requirements
Many businesses today are prioritising digitisation, driven both by the need to boost internal efficiency and the pressure to comply with a growing number of e-invoicing regulations. Although digitisation offers advantages such as greater accuracy, setting up certain e-invoicing tools – specifically protocol connectors (the digital pipelines that transmit, validate, and deliver invoices across platforms and tax authorities) – can be a complicated process, and one that often results in delays, inefficiencies, and increased operational risk.
Why are protocol connectors crucial e-invoicing tools?
E-invoicing protocol connectors are technical integrations that allow invoice data to be exchanged between systems in a compliant, secure, and automated way. They are the linchpins of the e-invoicing process, especially in countries adopting continuous transaction control (CTC) models, where real-time or near-real-time validation by tax authorities is mandatory.
Without properly configured connectors, the e-invoicing workflow breaks down. These connectors help in tasks such as authenticating credentials and then transmitting data to and from intermediaries or government platforms. They are essential for ensuring that an invoice reaches its destination in a compliant form.
What does a typical e-invoicing flow look like?
To appreciate the critical role of protocol connectors in global e-invoicing, it’s essential to understand how an invoice travels through the system in countries employing a CTC clearance and centralised model, such as Poland, Romania, and Hungary. These frameworks mandate a highly structured, real-time exchange of invoice data between suppliers, intermediaries, tax authorities, and buyers.
- Step 1: Invoice creation in the ERP system
The process begins with the supplier generating an invoice within their ERP or financial software. At this stage, compliance with local tax codes, field-level requirements, and document formatting is essential. While the invoice exists digitally, it is not yet compliant until it has been validated by national authorities – a step that hinges on subsequent data transmission enabled by protocol connectors.
- Step 2: Transmission to the integration platform (via ERP connectors)
Rather than submitting the invoice directly to the government platform, it is passed to an integration layer, such as ecosio’s managed service. Here, protocol connectors perform several critical technical functions:
- Authentication: Confirming the identity and authority of the sending party
- Data transformation: Converting the invoice from ERP-native formats to the schema required by the specific national platform (e.g., XML for KSeF or ANAF)
- Secure transport: Managing communication protocols such as AS4, REST API, or SFTP to ensure encrypted, tamper-proof data exchange
The connector acts as a real-time translator, courier, and gatekeeper, ensuring the invoice is properly prepped and transmitted under the right parameters.
- Step 3: Submission to the government platform via an authorised intermediary
Once formatted and packaged, the invoice is submitted to the centralised tax authority system through an intermediary explicitly authorised by the supplier. This intermediary may be a third party or, in many cases, the integration platform provider itself. The protocol connector remains active in this step, managing session handling, error feedback loops, and ensuring message integrity.
Government systems such as Romania’s ANAF, Poland’s KSeF, and Hungary’s NAV require exacting standards for submission. The protocol connector ensures these standards are met, right down to the required headers, tokens, and cryptographic signatures.
- Step 4: Validation or clearance by the tax authority
Upon successful receipt, the invoice undergoes validation by the tax authority. This may include syntax checks, VAT ID verification, or structural conformity with local compliance rules. Depending on the CTC model, the authority may also assign a clearance ID, signature hash, or digital stamp.
While this validation happens outside the connector, the connector is responsible for relaying clearance statuses and official metadata back to the sender or onward to the buyer. It ensures that the feedback loop is uninterrupted and properly logged—often integrating directly into the ERP to reflect updated document statuses.
- Step 5: Invoice delivery to the buyer
After clearance, the approved invoice is delivered to the buyer. Delivery may be executed by the tax authority or relayed back through the integration platform. In some jurisdictions, the invoice will carry government-issued metadata, such as clearance stamps or timestamps, indicating successful processing.
Once again, the protocol connector ensures the invoice and any additional compliance artifacts (such as clearance codes or timestamps) are securely delivered to the appropriate recipient system – be it another ERP, archive system, or downstream accounting tool.
The strategic role of protocol connectors in CTC compliance
Across every stage of the CTC e-invoicing lifecycle, protocol connectors act as the central nervous system. They do more than just “connect systems”…
- They actively enforce technical compliance, provide traceability, and reduce the risk of failed transactions
- They bridge complex systems and national platforms with real-time adaptability
- They minimise manual intervention, making compliance repeatable and scalable
- They enable auditable, secure communication channels aligned with national and international data security standards
In CTC environments, where delays, rejections, or invalid formats can result in regulatory penalties or revenue disruption, a well-implemented protocol connector isn’t just helpful; it’s essential.
Common connector issues
Delays
For example, a delay in invoice clearance due to improperly mapped XML fields can cause significant disruption to the order-to-cash cycle, particularly in just-in-time supply chains where payment triggers are tightly linked to invoice approval.
Rejections
A rejection stemming from missing authentication tokens can require manual intervention and resubmission, leading to bottlenecks.
Compliance breach
A compliance breach, such as failure to include mandatory tax identification elements, can not only halt invoice processing, but also expose the business to fines, audits, and reputational damage.
Challenges for enterprises
Challenges for business users: lost in translation
For business users, protocol connectors often feel like a technical black box. They know that successful setup is essential to meet compliance requirements and enable invoice automation, yet they rarely understand the technical details.
This lack of visibility leads to a range of challenges, including:
- Knowledge gaps: Most business users aren’t familiar with protocols like AS4, SFTP, or REST APIs, which are often required to establish secure, real-time connections with tax authorities or intermediaries.
- Manual communication: Historically, the exchange of sensitive setup details (like endpoint URLs, certificates, or authentication credentials) has taken place via insecure, manual methods such as email or internal chat. This not only slows down implementation but also increases the risk of errors and data breaches.
- Dependency on IT or external vendors: Without a self-service option, business teams are entirely reliant on technical staff or third-party providers, which can easily lead to delays, miscommunication, and unnecessary costs.
Challenges for technical users: missing the business context
On the other hand, while technical users may be well-versed in API integrations or ERP configuration, that doesn’t mean they’re equipped to handle e-invoicing protocol connectors. For technical users, the challenge lies not in technical execution, but in understanding what needs to be implemented for compliance in each specific country.
Key pain points include:
- Unclear or incomplete requirements: Different countries have vastly different rules and formats for e-invoicing, often buried in hard-to-navigate government websites or fragmented documentation.
- Lack of end-to-end guidance: Without clear, actionable steps tied to each country’s compliance model, IT teams are left piecing together information, risking missteps that can delay or derail deployment.
- Cross-functional bottlenecks: IT often needs input from finance or legal teams to ensure proper invoice content or tax requirements, creating organisational friction and slowing down projects.
Complexity multiplier: navigating CTC model requirements
The global shift towards Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) is intensifying the pressure created by the surge of e-invoicing mandates. In CTC models, invoice data must be sent to and validated by a tax authority before it reaches the buyer. This introduces a real-time compliance requirement, making robust and accurate protocol integration essential.
Countries such as Romania (RO e-Factura), Poland (KSeF), and Malaysia (MyInvois) already mandate or plan to mandate CTC frameworks. These systems require:
- Precise, secure API connections with central government platforms
- Automated credential handling using government-issued tokens or digital certificates
- Detailed format mapping to ensure the invoice conforms to national standards (often XML-based)
For multinational enterprises, this means managing multiple, often inconsistent connection protocols across countries, which can overwhelm even experienced technical teams.
The ecosio solution: self-service country connectors
To address these issues, ecosio has introduced e-invoicing tools purpose-built for real-world challenges: self-service country connectors. These connectors offer structured, guided support within the ecosio Monitor, making it easier for both technical and business users to establish efficient and reliable e-invoicing connections with selected countries.
What sets ecosio’s approach apart:
- User-friendly design tailored to both tech-savvy users and business stakeholders
- Step-by-step country-specific guidance with screenshots and checklists carefully tailored by our e-invoicing specialist team
- Pre-validated connection points that streamline integration and minimise trial-and-error
Whether you’re onboarding to Romania’s ANAF system, Poland’s KSeF, or Hungary’s NAV (the countries where ecosio’s Self Service connectors are already available), the goal is the same: reduce friction, boost confidence, and accelerate your compliance journey.
ecosio’s self-service country connectors make this possible by replacing manual credential exchange with a guided interface tailored to each country’s regulatory requirements. In Hungary and Poland, this structured approach improves efficiency and reduces errors, while in Romania, it provides added automation to further simplify onboarding and faster integration with ANAF.
Designed to eliminate confusion and manual back-and-forth, these e-invoicing tools empower users to manage complex e-invoicing mandates confidently and independently. By delivering country-specific clarity and streamlined setup processes, ecosio helps businesses minimise risk, adapt quickly to evolving regulations, and focus on what matters most – achieving full e-invoicing compliance with speed and precision.
Why this matters
The difference between a well-implemented e-invoicing connector and a flawed one isn’t just technical – it’s strategic.
With ecosio’s approach:
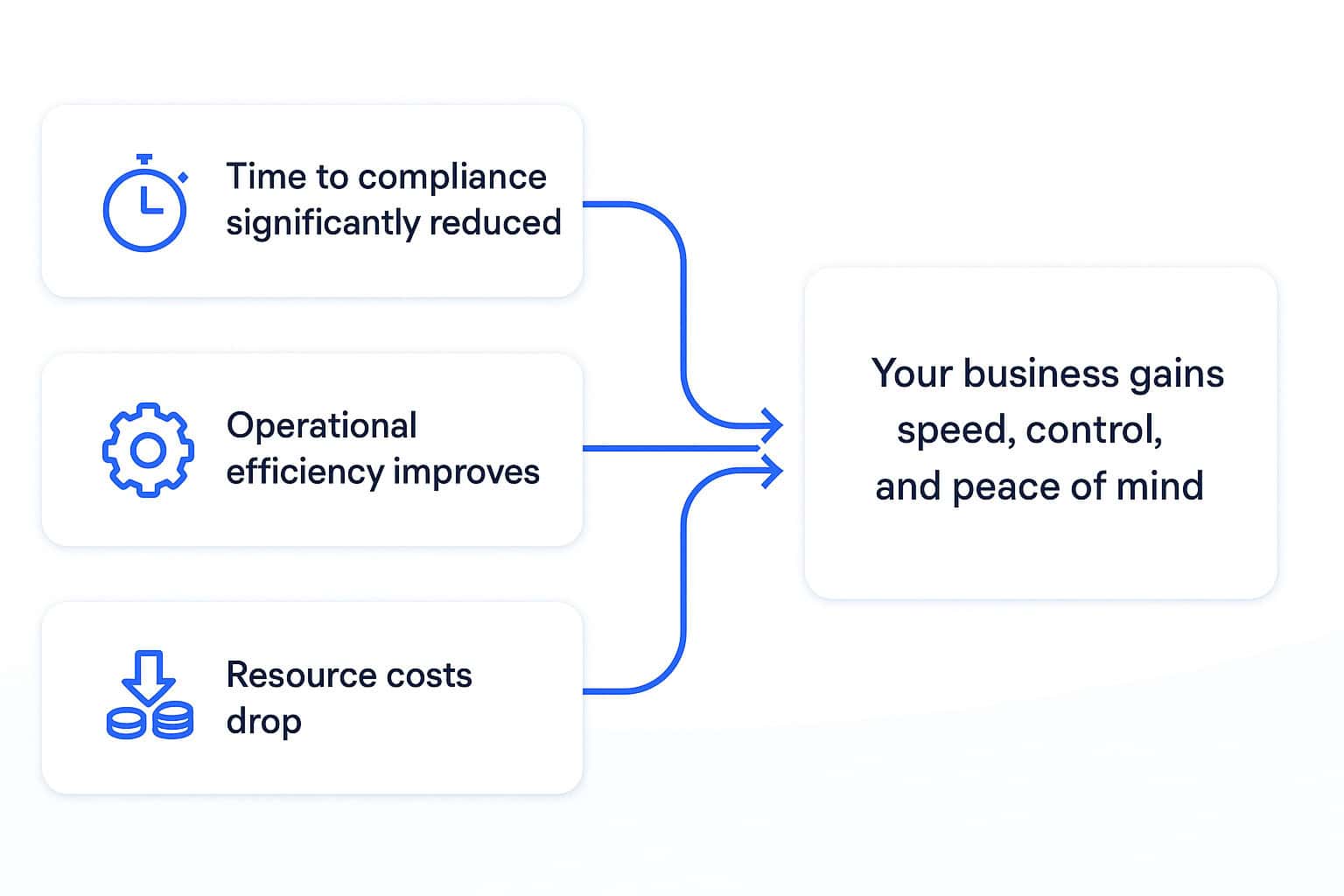
- Time to compliance is shortened, helping you avoid regulatory penalties.
- Operational efficiency improves, as teams waste less time troubleshooting and reworking failed connection implementation.
- Resource costs drop, reducing reliance on external service providers or overburdened internal teams.
Ultimately, your business gains speed, control, and peace of mind.
How to use self-service connectors in the ecosio Monitor
Setting up a supported protocol connector with ecosio Monitor is now a guided, intuitive process. Here’s how it works:
- Request the connector to be added to your ecosio Monitor instance: Contact the ecosio’s Onboarding and Operations team and request the connector to be provisioned for your instance, accessible in the “Connectors” section of the ecosio Monitor, ready for setup.
- Navigate to “Connectors”: Log in to ecosio Monitor and go to the “Connectors” section.
- Choose e-invoicing connectors: Select the appropriate setup option from the dashboard.
- Country-specific guidance: Based on your onboarding flow, the platform presents tailored documentation (e.g. Romania – ANAF guide) with detailed steps.
- Follow the instructions: Utilise the step-by-step comprehensive guidance – including credential requirements, and error handling tips – to complete your connector setup successfully.
Et voilá! Your connection is set up, you’re fully compliant and ready to send e-invoices. Try it yourself with our step-by-step demo:
Limitations to keep in mind
While ecosio’s self-service solution marks a major step forward, it’s important to acknowledge its current limitations:
- Limited country availability: At present, connectors are only available for select CTC-model countries, with more to follow.
- Not universal: Countries using decentralised or post-audit models (e.g. Germany and Belgium) are currently outside the scope of self-service documentation for now.
- Focus on CTC: E-invoicing tools are most valuable where direct API integration with government platforms is required.
Even with these limitations, the solution significantly reduces friction in some of the most complex regulatory environments.
The future of e-invoicing tools and processes: unified and user-centric
ecosio’s vision doesn’t stop at today’s capabilities. The roadmap for self-service country connectors includes:
- Expanded country coverage to match evolving mandates
- Simplified technical documentation to further ease implementation
- A smarter interface that adapts based on your country, business model, and ERP environment
The end goal? A fully unified and intuitive e-invoicing setup process that anyone can navigate, no matter their role or background.
Conclusion
E-invoicing protocol connectors are complex e-invoicing tools, but a critical component of compliance. For too long, they’ve been a source of frustration for both business and technical users. With the rise of CTC models and real-time validation requirements, this challenge will only grow.
Thankfully, it doesn’t have to be this way. With ecosio’s self-service country connectors, what was once a maze of uncertainty can become a fast, guided path to success.
Want more information?
If you’d like to see how protocol connectors could transform the efficiency of your EDI processes, why not speak to one of our EDI experts? We’re always happy to help!