Croatia’s Fiscalisation 2.0 reform introduces mandatory domestic B2B e-invoicing for VAT-registered businesses from 1 January 2026, and expands the existing B2G framework by adding fiscalisation and e-reporting obligations. Businesses must issue and receive structured e-invoices in UBL 2.1 aligned with Croatia’s CIUS, exchange them via secure access points and authorised information intermediaries, and separately submit fiscalisation and e-reporting data to the Croatian Tax Administration (Porezna uprava) using the Tax Authority’s dedicated XML formats. In this guide, we explain how the mandate works in practice and what companies can do to reduce compliance risk and operational disruption.
TL;DR summary
- From 1 January 2026, Croatia mandates domestic B2B e-invoicing and expands B2G requirements under Fiscalisation 2.0, requiring businesses to exchange structured invoices and separately report transaction data to the tax authority
- Compliance requirements: UBL 2.1 invoices with Croatia’s CIUS, secure exchange via access points or intermediaries, and digitally signed fiscalisation and e-reporting using OIB-linked certificates.
- Croatia requires three parallel processes: e-invoice exchange between parties, fiscalisation reporting by both issuers and recipients, and monthly e-reporting of rejected invoices (by recipients) and payments (by issuers).
- The Croatian model is operationally complex, as invoice exchange, fiscalisation, and monthly e-reporting run as parallel processes rather than a single clearance flow
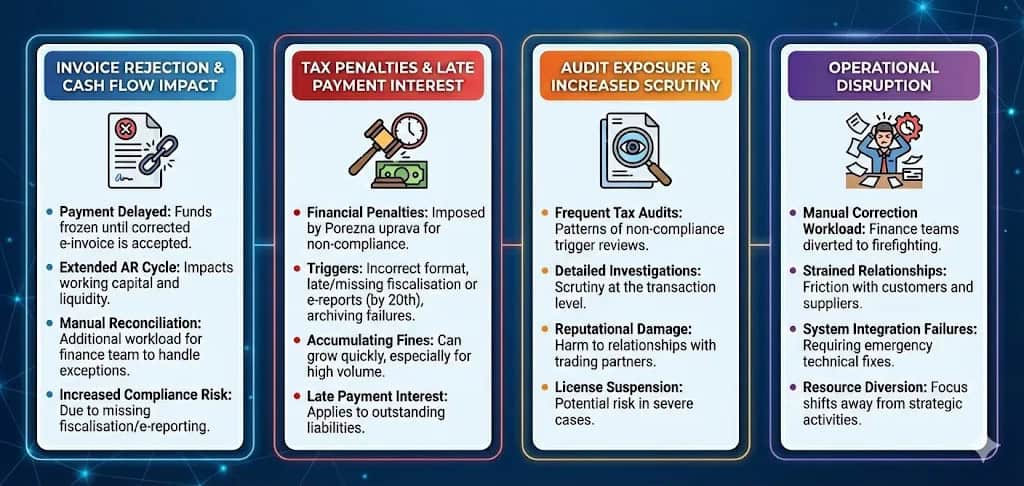
- Non-compliance can result in invoice disputes, delayed payments, financial penalties, and additional audit and reconciliation work
- Businesses can build and maintain in-house systems or partner with a managed compliance provider to reduce risk and effort
- Fully managed providers like ecosio offer certified e-invoicing compliance that simplifies exchange, fiscalisation, reporting, archiving, and ongoing regulatory changes through a single platform
E-invoicing in Croatia: an overview
Croatia’s mandatory e-invoicing system represents a significant evolution of its fiscalisation framework. Croatia is implementing a decentralised model that combines structured e-invoice exchange between trading partners with separate fiscalisation reporting and monthly e-reporting obligations.
Croatia’s Fiscalisation 2.0 introduces mandatory domestic B2B e-invoice exchange plus separate fiscalisation reporting and monthly e-reporting. The system is governed by Porezna uprava (Croatia’s tax administration) and requires businesses to navigate the three distinct but interconnected processes:
- E-invoice exchange: Structured invoices exchanged between trading partners via AS4 protocols through authorised information intermediaries and secure access points
- Invoice fiscalisation: Real-time reporting of outbound and inbound invoice data to Porezna uprava, separate from the exchange process
- E-reporting: Monthly submission of additional transaction data, where recipients report rejected e-invoices, and issuers report e-invoice payments and cases where an e-invoice could not be issued
For B2G transactions (mandatory since 1 January 2019), Croatia’s existing centralised platform Servis e-Račun za državu (operated by Fina) continues to function, with fiscalisation obligations added from 1 January 2026.
This multi-layered approach creates operational complexity: businesses must manage invoice generation, format validation, secure transmission, digital signature application, fiscalisation flows, and e-reporting deadlines simultaneously whilst maintaining ERP system stability and ensuring cash flow continuity.
Croatia’s e-invoicing journey: a timeline
Croatia has been progressively building its electronic invoicing and fiscalisation infrastructure over the past decade:
This phased rollout reflects Croatia’s methodical approach to digital tax transformation, allowing businesses time to adapt whilst building a comprehensive compliance infrastructure aligned with EU standards and the ViDA directive.
Why did Croatia move to mandatory e-invoicing?
Croatia’s fiscalisation 2.0 modernises tax administration, improves VAT compliance, reduces fraud, and enables real-time transaction visibility. Fiscalisation gives the tax administration near real-time visibility into invoice data, which supports monitoring and anomaly detection.
The reform also aligns Croatia’s digital tax controls with broader EU direction (including ViDA). However, cross-border invoices are currently outside the scope of the Croatian e-invoicing mandate.
How might current and upcoming regulations affect your business?
What happens if you’re not compliant?
Non-compliance with Croatia’s e-invoicing and fiscalisation requirements carries significant financial and operational risks:
How can your business achieve compliance in Croatia?
Companies facing e-invoicing mandates have tried two approaches that ultimately fail:
- DIY software: Buy platforms but your IT and Tax teams become regulation researchers and maintenance technicians instead of doing their actual jobs.
- Regional patchwork: Hire vendor A for Italy, B for France, C for Croatia. Result: five to six vendors, limited visibility, integration complexity, and no single owner when issues occur.
Businesses face a better choice: build and maintain everything with an in-house solution or partner with a fully managed e-invoicing provider, like ecosio.
Your two compliance options compared
| Build and maintain in-house | Use a fully managed e-invoicing provider | |
| What it involves |
|
Partnering with a managed compliance operations platform like ecosio that manages the entire e-invoicing and fiscalisation process:
|
| Timeline | Six to 12 months for the initial build, plus ongoing updates for each regulatory change | Faster onboarding led by e-invoicing experts, automatic regulatory updates included |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Challenges |
|
|
| Best suited for | Very large enterprises with substantial IT resources, single-country operations, and highly specific integration requirements that cannot be met by external platforms | Most businesses, particularly those with limited e-invoicing expertise, tight implementation timelines, multi-country operations or expansion plans, a preference for predictable costs over large capital expenditure, and a desire to focus internal resources on core business activities |
Hybrid approaches
Some large enterprises adopt hybrid models, handling certain processes in-house whilst outsourcing specific components like validation, transmission, or archiving. However, this requires careful orchestration to ensure compliance responsibility is clearly defined.
What most businesses choose
The vast majority of businesses opt for externally managed solutions, particularly when facing tight deadlines. The combination of regulatory complexity, dual compliance processes (exchange plus fiscalisation), and the need for certified intermediary status makes external partnerships the pragmatic choice.
How ecosio ensures stress-free compliance in Croatia
ecosio is proud to be officially certified by Porezna uprava as an information intermediary for Croatia’s e-invoicing system. We provide a managed compliance operations platform combining automation software with expert monitoring, maintenance, and issue resolution across global jurisdictions, enabling us to manage the complete compliance process on your behalf while you focus on your core tasks.
Why choose ecosio for e-invoicing Croatia?
Certified information intermediary status
We’re authorised to exchange e-invoices on your behalf, ensuring your transactions meet all technical and legal requirements from day one.
Dual-process management
We handle both e-invoice exchange (via AS4 protocols through secure access points) and separate fiscalisation flows with Porezna uprava, including digital signature application using OIB-linked certificates.
Automatic format compliance
Your ERP data is automatically validated and converted to UBL 2.1 XML with Croatia’s CIUS, preventing rejections and ensuring clean fiscalisation records.
E-reporting transmission
ecosio automatically transmits e-reporting messages based on customer-provided payment/rejection data, ensuring you meet the 20th of each month deadline.
Multi-country platform
If you operate across Europe or globally, ecosio provides a single managed compliance operations platform covering 40+ countries, reducing vendor sprawl and integration complexity.
Deep ERP integration
Production-grade integration patterns for SAP®, Microsoft Dynamics, Oracle, and other major ERP systems minimise internal engineering work and accelerate go-live.
Proactive regulatory updates
Our compliance experts monitor Croatian legislation continuously, implementing system updates before regulations change so you’re never caught off guard.
Proven reliability
Our high-availability infrastructure with built-in redundancy keeps your invoicing running continuously. ecosio has maintained zero downtime since 2012 and our customers report near-zero day-to-day involvement post go-live.
Frequently asked questions
Find answers to the most pressing questions about this mandate and get detailed technical specifications about Croatia from our Croatia e-invoicing country page.
Need help with Croatia e-invoicing compliance?
With the 1 January 2026 deadline, you must be compliant with the Croatia mandate.
Why act now? Croatia is one of 40+ countries implementing e-invoicing mandates. Treating compliance as managed infrastructure future-proofs your operations and turns regulatory pressure into competitive advantage.
ecosio’s certified intermediary status, multi-country platform, and ERP integration expertise ensure you meet Croatia’s requirements confidently whilst minimising internal resource demands. Whether implementing Croatia standalone or as part of a broader European programme, our team is ready to help you achieve worry-free compliance.
What can you do next:
- Contact our e-invoicing experts to discuss your specific requirements, timelines, and integration needs.
- Stay informed about e-invoicing changes across Europe by signing up for our e-invoicing updates newsletter, and receive regular regulatory briefings and compliance insights.


 **2026: Mandatory B2B e-invoicing for VAT-registered taxpayers (1 January)** All VAT-registered businesses must issue, exchange, and fiscalise domestic B2B and B2G e-invoices. Real-time fiscalisation obligations are added to existing B2G transactions. **2027: Extension to non-VAT registered taxpayers (1 January)** The mandate expands to non-VAT registered taxpayers liable for income or corporate tax, plus public sector bodies.](https://ecosio.com/app/uploads/2025/12/croatia-1.jpg)
). - Monthly submission of e-reports for rejected invoices, payment confirmations and cases where an e-invoice could not be issued electronically (non-issued e-invoices) - Archive invoices and fiscalisation confirmations for 11 years **Public sector entities** receiving B2G invoices must: - Submit required **e-reporting** data for B2G flows (including **rejection reporting** where applicable) within the monthly reporting cycle - Accept and process structured e-invoices - Fiscalise received invoices within five working days - Maintain compliant archiving systems ## **From 1 January 2027:** **Non-VAT registered taxpayers** liable for income or corporate tax, plus additional public sector bodies, must comply with the same requirements. ## **Exemptions and special cases:** **B2C transactions** remain outside the mandatory e-invoicing scope but must still be fiscalised regardless of payment method. **Cross-border transactions** (exports and imports) are currently excluded from the mandatory e-invoicing requirements. **Self-billing arrangements:** In self-billing scenarios, the buyer issues the invoice on behalf of the supplier. Fiscalisation must occur within five working days after invoice issuance.](https://ecosio.com/app/uploads/2025/12/croatia-2-graphic.jpg)