Various terms and concepts will crop up when data is exchanged with a SAP ERP system, whether communication is handled via in-house or external systems. This article discusses the relationship between IDocs, ALE, RFC and EDI in a SAP ERP system and points out which concepts to use and where.
IDoc – intermediate document
IDocs is the standard exchange format used for importing/exporting data into/from SAP systems. Business data such as master data, invoices, delivery notes etc. may be exchanged with external systems via IDoc interfaces. These external systems may be within your own company or data may be exchanged with systems belonging to other companies.
An IDoc interface has a defined data structure and IDoc processing logic.
The SAP term for data exchange with other in-house systems is ALE (or Application Link Enabling). The term EAI stands for Enterprise Application Integration and is also commonly used in non-SAP environments. ALE communication may be synchronous or asynchronous.
Data exchange to other companies is referred to as Electronic Data Interchange, or EDI. EDI communication is message-based and thus always asynchronous.
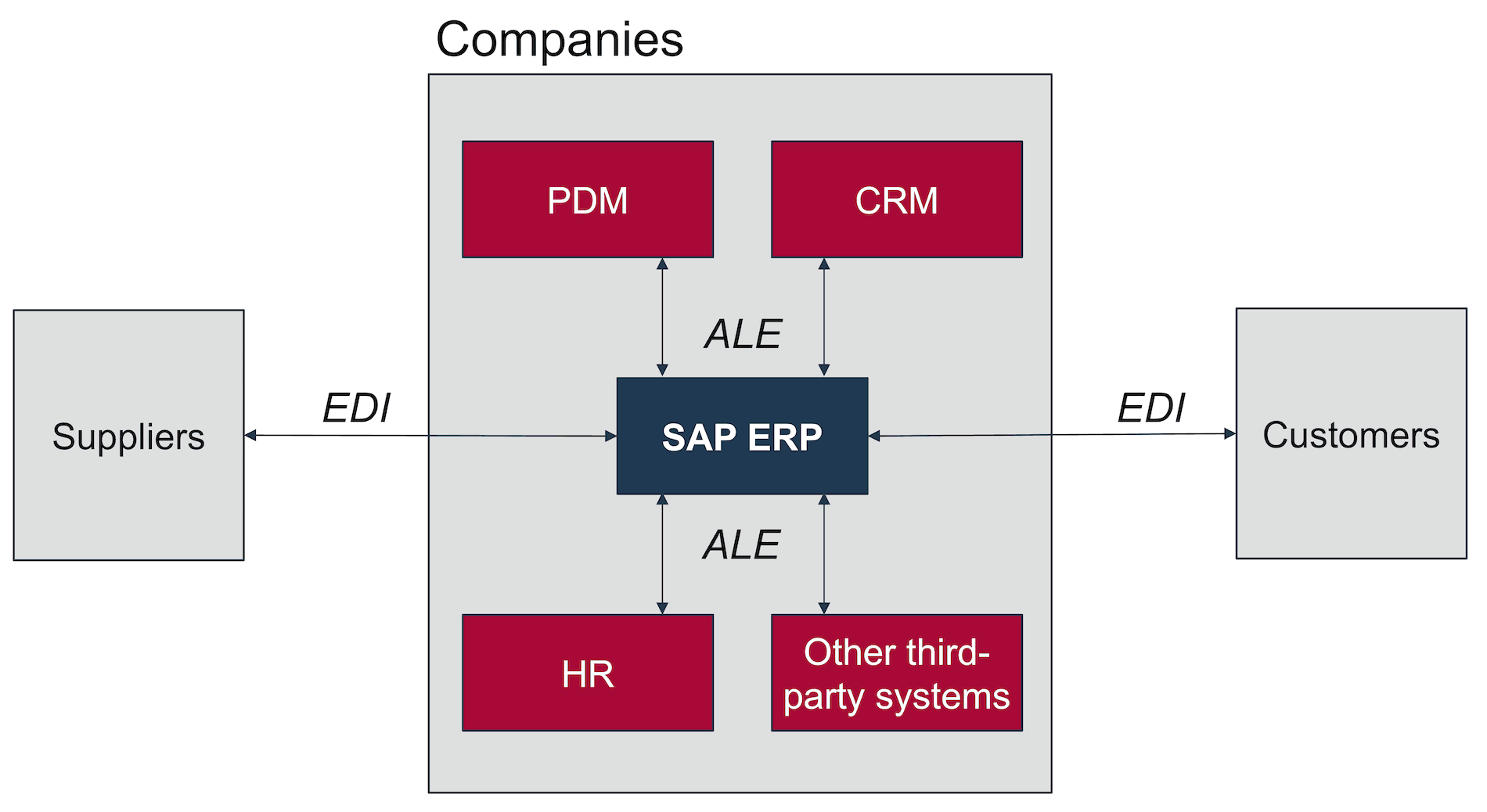
The figure below shows an example of a scenario with ALE and EDI.
Difference between ALE and EDI
Customers and suppliers are linked to the SAP system via EDI. In-house third-party software such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management), HR (Human Resources) and PDM (Product Data Management) will be linked via ALE.
ALE – application link enabling
Within the ALE framework, business processes take place across different in-house IT systems. The systems are physically separate, and communication takes place between different Logical Systems (LS).
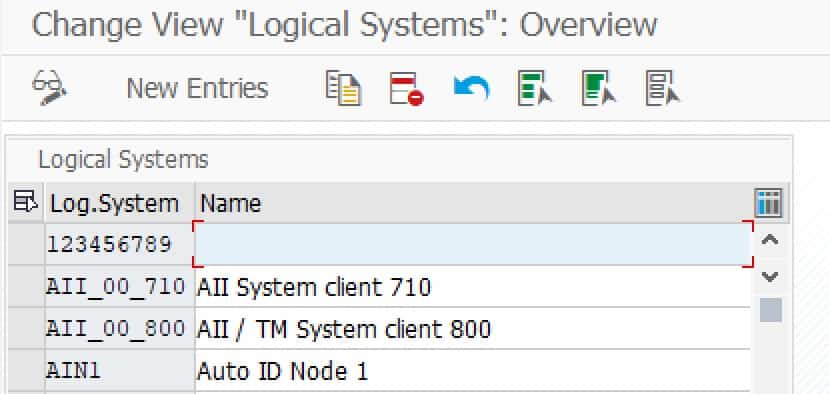
A logical system is comprised of specific software such as CRM systems. In SAP, a logical system is assigned to a client and has an own system name. Logical systems may be defined in SAP using Transaction BD54, as shown in the figure below.
Logical systems in Transaction BD54
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
Specific clients are assigned to a logical system via Transaction SCC4.
A distribution model must be set up to define which IDocs to exchange using which logical system. A distribution model may be defined using Transaction BD64.
ALE is based on RFC (Remote Function Call) for communication.
RFC – Remote Function Call
RFC is another commonly seen EDI acronym and stands for Remote Function Call. RFC a process used to call up a function (also referred to as function module in SAP) in a remote system. Business logics may thus be called up in a third-party system.
In the SAP environment RFC is effectively synonymous with Remote Procedure Call (RPC), but it is also used as an umbrella term for SAP interfaces and protocols used for the implementation of function calls.
A DESTINATION parameter is given when calling up a remote function module in ABAP. The following is an example of a call-up of the STORE_NEW_CUSTOMER function in the CRM4711 system.
CALL FUNCTION 'STORE_NEW_CUSTOMER'
DESTINATION 'CRM4711'
EXPORTING
customer = cust
IMPORTING
crm_customer_id = id
EXCEPTIONS
customer_exists = 1
A customer object is passed to this method, to store in the CRM system. The CRM system customer ID number is returned to, for instance, store with the master debtor data in the SAP system.
SAP distinguishes between four different types of RFCs:
- Synchronous (sRFC)
- Asynchronous (aRFC)
- Tranactional (tRFC)
- Queued (qRFC)
EDI – Electronic Data Interchange
Data exchange with other companies is referred to as EDI (Electronic Data Interchange). Instead of the direct exchange of IDocs, data will first be converted to a uniform exchange format, the so-called EDI format. Well known EDI formats include, for instance, UN/EDIFACT, ANSI ASC X12, VDA etc. and the corresponding derivatives and sub-standards.
An EDI converter is used for conversion between IDocs and the EDI format.
SAP systems do not use logical systems for electronic data exchange, but they define partners. These partners may, for instance, be customers or suppliers. The settings for specific partners are also called partner agreements and configured in Transaction WE60.
Any questions about SAP, IDocs, ALE, RFC or EDI?
Do you have any questions about SAP ERP, SAP SD and the associated EDI processes? Please contact us or check out our chat – we look forward to assisting you!
Alternatively, please see our resources section to check out some of our many helpful webinars, infographics and white papers!
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.